Targeted protein degradation in the transmembrane and extracellular space | Science
Transmembrane and extracellular proteins are essential components of cellular architecture and function, significantly influencing how cells communicate and interact with their environment. These proteins are embedded in cellular membranes or exist outside the cell, facilitating a myriad of processes such as signal transduction, immune responses, and cell adhesion. Their roles are particularly critical in the context of various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. For instance, aberrations in the signaling pathways mediated by these proteins can lead to uncontrolled cell growth or immune system dysfunction, underscoring their importance in both disease progression and treatment strategies.
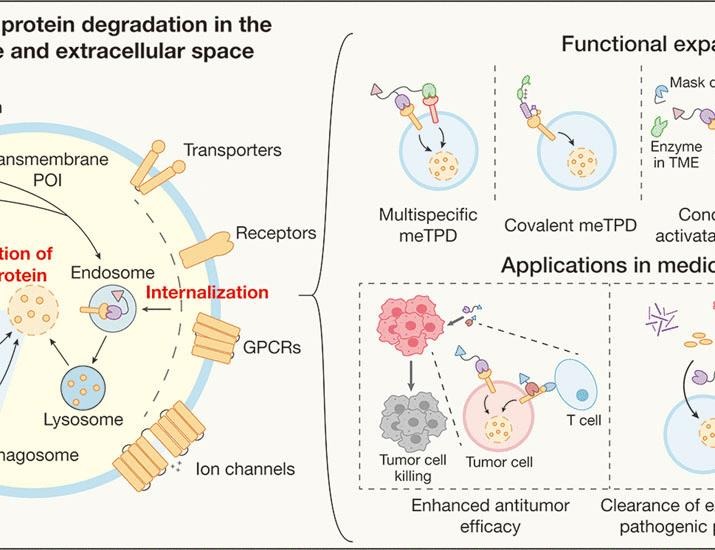
One of the innovative approaches in modern therapeutics is targeted protein degradation (TPD), which aims to selectively eliminate malfunctioning or harmful proteins from cells. TPD utilizes small molecules, often referred to as degraders, that can bind to specific proteins, marking them for destruction by the cell’s ubiquitin-proteasome system. This strategy not only offers a way to tackle diseases caused by overexpressed or mutated proteins but also helps in minimizing side effects associated with traditional therapies that may indiscriminately affect healthy proteins. For example, in cancer treatment, TPD can be employed to degrade oncogenic proteins that drive tumor growth, providing a more precise and potentially less toxic approach to therapy. As research continues to evolve, the integration of TPD with a deeper understanding of transmembrane and extracellular protein functions could lead to breakthroughs in the treatment of complex diseases, paving the way for more effective and targeted therapeutic options.
In summary, the interplay between transmembrane and extracellular proteins and targeted protein degradation represents a promising frontier in biomedical research. By harnessing the specific roles these proteins play in cellular communication, scientists are developing innovative strategies to combat diseases at their core. This approach not only highlights the importance of protein interactions in health and disease but also exemplifies the potential of modern therapeutic techniques to revolutionize treatment paradigms. As we continue to uncover the intricacies of cellular processes, the future of medicine may very well hinge on our ability to manipulate these fundamental biological mechanisms.
Transmembrane and extracellular proteins play crucial roles in diverse cellular functions and communication, affecting the progression and treatment of various diseases by mediating vital cellular processes. Whereas targeted protein degradation (TPD) …
Eric
Eric is a seasoned journalist covering Health news.