Hepatic leukemia factor directs tissue residency of proinflammatory memory CD4+ T cells | Science
**Understanding the Role of Hepatic Leukemia Factor in CD4+ TRM Cell Differentiation**
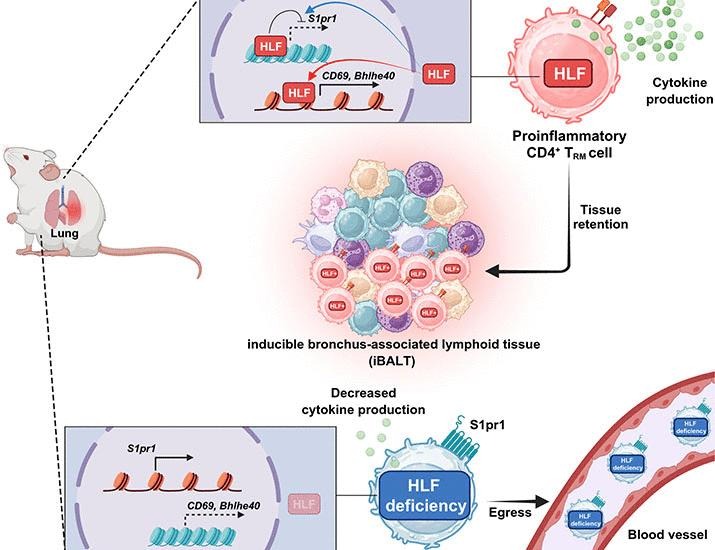
Recent research has shed light on the differentiation of CD4+ tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells, which play a pivotal role in both host defense mechanisms and the development of chronic inflammatory diseases. These immune cells are crucial for providing long-lasting protection against pathogens, as they reside in tissues and can respond swiftly to reinfections. However, the molecular signals that guide their differentiation remain largely elusive. A significant breakthrough in this area has been made by identifying the transcription factor hepatic leukemia factor (HLF) as a key player in the differentiation process of CD4+ TRM cells.
In the study, researchers utilized various experimental models to explore how HLF influences the development of TRM cells. They discovered that HLF is essential for the expression of specific genes that drive the differentiation of CD4+ T cells into TRM cells. For instance, the absence of HLF resulted in a marked reduction of TRM cells in tissues, which in turn compromised the immune system’s ability to mount a robust response against previously encountered pathogens. This finding is particularly relevant in the context of chronic inflammatory diseases, where the dysregulation of TRM cell differentiation can exacerbate conditions such as autoimmune disorders or chronic infections.
Moreover, the implications of this research extend beyond basic immunology. By understanding the role of HLF in TRM cell differentiation, scientists may uncover new therapeutic targets for treating chronic inflammatory diseases. For example, manipulating HLF activity could potentially enhance TRM cell responses in vaccination strategies, leading to improved immunity against infectious diseases. Conversely, inhibiting HLF could provide a novel approach to dampening excessive TRM cell activity in autoimmune conditions. This duality underscores the importance of HLF in both promoting effective immune responses and mitigating pathological inflammation, highlighting its potential as a critical target in future immunotherapeutic interventions.
CD4+ tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells contribute to host defense and to the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases, but the molecules that direct their differentiation are unknown. We found that the transcription factor hepatic leukemia factor …